The County Government’s role either be neglect for achievement country’s goals. As the population increases globally, new challenges are faced by countries. The well and pre-planned structure for utilizing natural and human-made resources is the key point for better achievements. For this role of local governments remains important and useful in shaping the lives of citizens. County governments, in particular, hold significant influence in various aspects of administration, development, and public service provision.
These local bodies are responsible for a wide range of services that directly impact citizens’ lives as well as Understanding the structures, functions, and challenges of county governments is essential for comprehending the dynamics of local governance.
We’ll delve into the county governments of the top countries, exploring their functions, structures, and contributions to their respective societies.
Understanding County Governments
What is a County Government?
A county government is a local administrative body responsible for governing a specific geographical area within a country. It serves as an intermediary between the central government and municipalities, ensuring the effective implementation of policies and programs tailored to the region’s needs.
Functions of County Governments
County governments are entrusted with various functions, including public safety, healthcare, education, infrastructure development, providing County Integrated Development Plan and environmental protection. They work towards enhancing the quality of life for residents by addressing local challenges and fostering community growth.
County Government Structures
Local Councils and Representatives
At the heart of county governance are local councils and representatives. These elected officials advocate for the interests of their constituents and make decisions on matters such as budget allocation, policies, and local regulations.
Administrative Divisions
Counties are often divided into smaller administrative units, such as districts or municipalities. This division facilitates efficient service delivery and allows county governments to address the unique needs of different areas within their jurisdiction.
County Governance Models
Centralized County Governance
In some countries, county governments operate under a centralized model, where decision-making authority is concentrated in the hands of the central government. This model ensures uniformity in policies but may lead to challenges in addressing local nuances effectively.
Decentralized County Governance
Conversely, decentralized county governance grants more autonomy to local governments. This approach enables tailored solutions to local issues but requires effective coordination between the central and local levels of governance.
Roles and Responsibilities
Legislative Functions
The legislative arm of the county government typically comprises elected officials responsible for enacting local laws, ordinances, and policies that resonate with the county’s distinct character.
Executive Functions
The executive branch executes the laws and policies set by the legislative body. The county executive, often elected separately, oversees the administration of various departments and ensures the efficient implementation of initiatives.
Administrative Functions
The administrative functions of the county government encompass a spectrum of services, including public safety, Land Use control, public health, Urban Management, transportation, and more. These services are designed to meet the essential needs of residents.
County Officials
Board of Commissioners
The Board of Commissioners, also known as the County Board, is a group of elected officials responsible for representing the interests of the county’s residents. They play a crucial role in decision-making, budget approval, and policy formulation.
County Executive
The County Executive, distinct from the Board of Commissioners, is the chief executive officer of the county. This individual oversees day-to-day operations, implements policies, and manages the county’s various departments.
Sheriff and Law Enforcement
The county sheriff’s office is tasked with maintaining law and order within the county. Sheriffs and their deputies ensure public safety and uphold the rule of law.
County Clerk
The County Clerk is responsible for maintaining official records, such as property deeds, marriage licenses, and election results. This role is pivotal for transparency and accountability.
County Treasurer
The County Treasurer manages the county’s finances, including the collection and disbursement of funds. This role ensures that the county’s financial operations are conducted smoothly.
Financing County Governments
Revenue Sources
County governments rely on various revenue sources, including property taxes, grants from the central government, user fees, and fines. These funds are crucial for maintaining infrastructure and providing essential services.
Budget Allocation
Budget allocation is a critical aspect of county governance. Elected officials determine how funds are distributed among different sectors, aiming to maximize benefits for the community.
County Services and Development
Healthcare and Social Services
County governments are often responsible for healthcare facilities, clinics, and social service programs. They ensure that residents have access to quality healthcare and support systems.
Education and Infrastructure
Education infrastructure, including schools and vocational training centers, falls under the purview of county governments. They also oversee the development and maintenance of local infrastructure, such as roads and public buildings.
Challenges Faced by County Governments
Intergovernmental Relations
Coordinating with central governments and other local entities can be complex. Effective intergovernmental relations are crucial for seamless service delivery and resource allocation.
Balancing Local Needs
County governments face the ongoing challenge of balancing the diverse needs of their residents, from rural agricultural areas to urban centers, ensuring equitable development.
Managing Growth and Development
As populations grow, counties must manage urban sprawl, environmental concerns, and infrastructure demands to create sustainable living environments.
Ensuring Accountability
Transparency and accountability are paramount for maintaining the public’s trust. County governments must implement measures that allow citizens to engage with and oversee their actions.
Innovative Solutions
Public-Private Partnerships
Many county governments are turning to public-private partnerships to fund and manage projects. These collaborations leverage private sector expertise while easing the financial burden on public resources.
Technological Advancements
Embracing technological advancements enhances service delivery and transparency. Digital platforms for citizen engagement, e-governance, and data analytics contribute to improved governance outcomes.
County Governments: Global Examples
Let’s take a closer look at how county governments operate in some of the top 20 countries worldwide:
- United States: Counties have significant authority over local affairs, including law enforcement and public health.
- China: County governments are responsible for implementing national policies and promoting economic development.
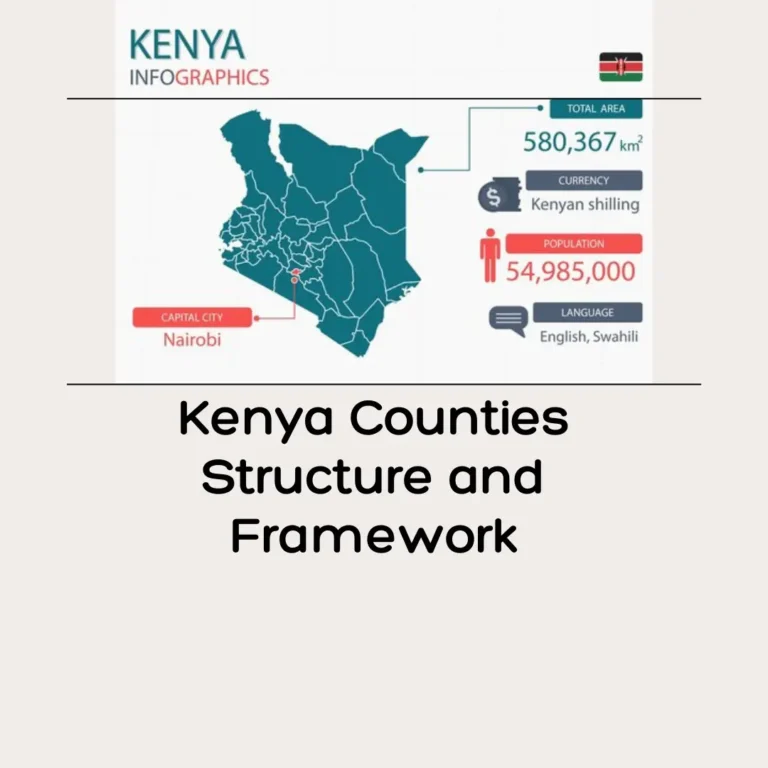
- Kenya: The total number of kenya Counties is 47, covering the structure and framework of whole country.
- India: District administrations play a crucial role in local governance, focusing on development and welfare programs.
- Brazil: Counties, known as “municipalities,” are responsible for healthcare and education.
- Germany: Counties, or “Kreise,” handle administrative and public services.
- United Kingdom: Counties manage local services like education and transportation.
Conclusion
County governments serve as the backbone of local governance, tailoring solutions to the unique needs of their communities. As we’ve explored, these entities play an important role in enhancing citizens’ quality of life through effective service delivery and development initiatives.
What is the primary role of a county government?
County governments primarily focus on governing a specific geographical area within a country, providing essential services and infrastructure.
How do county governments generate revenue?
County governments rely on revenue sources such as property taxes, grants, user fees, and fines to fund their operations.
What challenges do county governments face in terms of financing?
Limited financial resources and competing demands for funding often pose challenges for county governments.
What is the difference between centralized and decentralized county governance?
Centralized governance involves decision-making authority at the central level, while decentralized governance grants more autonomy to local governments.
How can technology benefit county governance?
Technology can improve transparency, citizen engagement, and service delivery through e-governance platforms and data-driven decision-making.