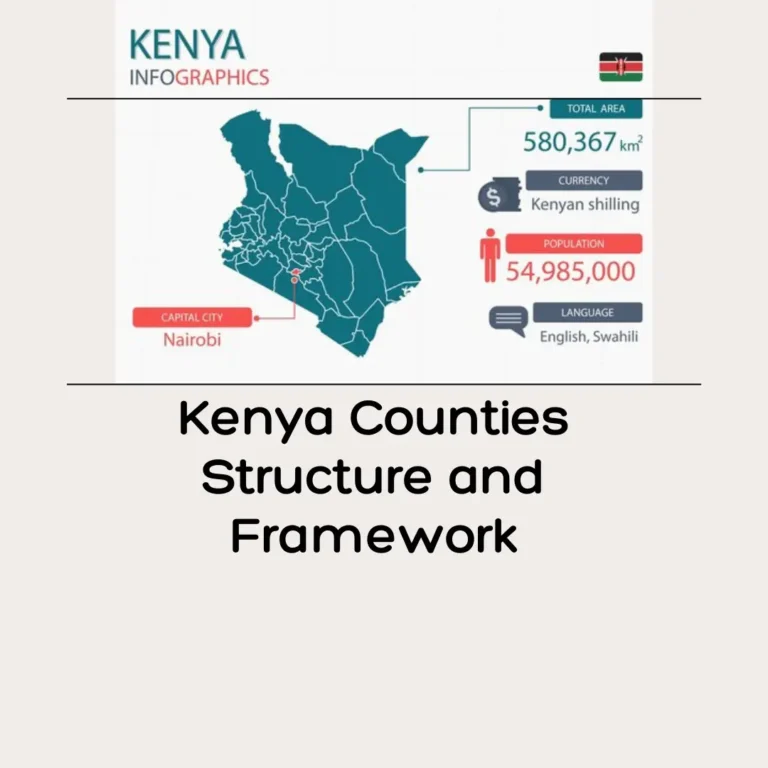
The County Integrated Development Plan (CIDP) is a strategic document that plays a vital role in guiding the development agenda of a county. It outlines the objectives, policies, programs, and projects that will drive sustainable development, Land use Planning within a specific geographical area. A comprehensive overview of the County Integrated Development Plan includes its importance, and how it influences the growth and progress of a county mentioned in detail.
The County Integrated Development Plan serves as a guideline and roadmap for counties through which they achieve their development goals, help in Urban Property Management as well as improve the quality of life for their residents. It is a comprehensive and participatory process that involves multiple stakeholders, including county governments, local communities, civil society organizations, and development partners.

Understanding the County Integrated Development Plan
The County Integrated Development Plan is a medium-term planning framework that covers a period of five years. It provides a clear and understandable vision for the county’s development, through which aligning it with national development priorities and the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). The plan takes into account the county’s unique characteristics, resources, and challenges, and proposes strategies to address them.
Components of a County Integrated Development Plan (CIDP)
A well-structured County Integrated Development Plan (CIDP) consists of several key components. These include:
1. Vision Statement
The vision statement articulates the long-term development aspirations of the county. It captures the desired future state that the county aims to achieve.
2. County Profile
The county profile provides an overview of the county’s geographical, social, economic, and cultural characteristics. It helps in identifying the county’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
3. Development Objectives
The development objectives outline the key areas where the county intends to focus its efforts. These objectives are derived from the county’s vision and are aligned with national development goals and priorities.
4. Sectoral Strategies and Programs
The County Integrated Development Plan (CIDP) identifies various sectors such as agriculture, health, education, infrastructure, tourism, and others. It formulates strategies and programs specific to each sector to promote their development and address existing challenges.
5. Resource Mobilization Plan
The resource mobilization plan outlines the financial requirements for implementing the County Integrated Development Plan (CIDP). It identifies potential sources of funding, both internal and external, and proposes mechanisms for mobilizing resources.
6. Implementation Framework
The implementation framework specifies the roles and responsibilities of various stakeholders involved in the execution of the CIDP. It also outlines the institutional arrangements and coordination mechanisms necessary for effective implementation.
Practical Steps County Governments Need to Take
County governments play a crucial role in the administration and development of regions within a country. To ensure effective governance and efficient service delivery, county governments must take several practical steps. Here are some essential actions they should consider:
1. Transparent Governance:
County governments should prioritize transparency in all aspects of their operations. This includes budgeting, procurement, decision-making processes, and public services. Openly sharing information with citizens builds trust and fosters a sense of accountability.
2. Citizen Participation:
Encourage and facilitate citizen engagement in governance. County governments should actively seek public input on important decisions, development projects, and policy-making. Public forums, town hall meetings, and online platforms can be utilized for this purpose.

3. Strengthening Local Institutions:
Invest in capacity building for local institutions and empower them to effectively carry out their roles. This includes providing training, resources, and support to elected representatives, civil servants, and community leaders.
4. Effective Public Service Delivery:
Focus on improving public service delivery in key sectors such as education, healthcare, infrastructure, and sanitation. Regularly assess and monitor the quality of services to ensure they meet the needs of the citizens.
5. Financial Management:
Maintain prudent financial management practices, including responsible budgeting and expenditure control. County governments should strive to enhance revenue collection while ensuring proper allocation of funds to priority projects.
6. Infrastructure Development:
Invest in the development and maintenance of infrastructure, such as roads, bridges, public transportation, and utilities. This improves connectivity, enhances economic growth, and raises the quality of life for residents.
7. Promoting Local Economy:
Support local businesses and entrepreneurs to stimulate economic growth and create job opportunities within the county. This can be done through incentives, capacity building, and fostering a business-friendly environment.
8. Health and Environment:
Prioritize public health initiatives and environmental conservation efforts. County governments should invest in healthcare facilities, disease prevention programs, waste management, and sustainable practices to protect the well-being of the population.
9. Education and Skill Development:
Emphasize the importance of education and skill development. Invest in schools, vocational training centers, and adult education programs to equip citizens with the necessary skills for employment and personal growth.
10. Security and Safety:
Collaborate with national security agencies to maintain peace and security within the county. Implement community policing strategies and invest in disaster preparedness measures to safeguard citizens from various threats.
11. Promote Tourism and Culture:
Capitalize on the county’s unique cultural heritage and natural attractions to promote tourism. This can contribute significantly to the local economy and provide employment opportunities.
12. Data and Technology:
Utilize data and technology to improve governance and service delivery. Implement e-governance initiatives, use data analytics for evidence-based decision-making, and improve data collection to monitor progress and identify areas for improvement.
13. Collaboration with Other Counties:
Foster collaboration and knowledge-sharing with other county governments to learn from each other’s successes and challenges. This can lead to innovative solutions and a more coordinated approach to regional development.
By taking these practical steps, county governments can enhance their effectiveness, responsiveness, and efficiency, ultimately leading to improved living conditions and a better quality of life for their citizens.
The Importance of County Integrated Development Plan (CIDP)
The County Integrated Development Plan holds immense significance for the development of a county. Here are some key reasons why CIDPs are crucial:
01. Holistic Development:
The CIDP takes a comprehensive approach to development, considering various sectors and their interlinkages. It ensures that development initiatives are well-coordinated and aligned with the overall vision of the county.
02. Local Contextualization:
The CIDP recognizes the unique characteristics and needs of each county. It allows for the customization of development strategies to address specific challenges and harness local resources effectively.
03. Public Role:
The CIDP process encourages citizen engagement and participation. It gives residents a platform to voice their opinions, contribute ideas, and shape the development agenda of their county.
04. Accountability and Transparency:
The CIDP promotes accountability by clearly defining the roles and responsibilities of stakeholders. It enhances transparency in resource allocation and utilization, fostering public trust and confidence in the county government.
05. Long-Term Vision:
By setting a clear vision and development objectives, the CIDP ensures that the county’s development efforts are guided by a long-term perspective. It helps avoid ad-hoc decision-making and provides continuity across political administrations.

Development Priorities and Strategies
Each county’s CIDP identifies specific development priorities and strategies based on its unique context. These priorities can range from infrastructure development, job creation, poverty alleviation, healthcare improvement, education enhancement, environmental conservation, and more. The strategies include policy interventions, programs, and projects that will be implemented to achieve the identified priorities.
Stakeholder Engagement in the County Integrated Development Plan (CIDP) Process
The CIDP process is highly participatory, involving various stakeholders throughout its development. County governments actively engage with local communities, civil society organizations, private sector entities, and development partners to gather input, build consensus, and ensure a sense of ownership among all stakeholders. This collaborative approach increases the chances of successful implementation and sustainable development outcomes.
Challenges and Solutions
Implementing a CIDP is not without its challenges. Limited financial resources, capacity constraints, and coordination issues are common hurdles faced by counties. However, by adopting innovative financing mechanisms, strengthening institutional capacities, and enhancing coordination among stakeholders, these challenges can be overcome.
| Challenges | Solutions |
| Limited financial resources | Exploring alternative funding sources such as public-private partnerships Engaging with development partners and seeking external funding Prioritizing projects and allocating resources efficiently |
| Capacity constraints | Investing in training and capacity-building programs for county government officials Collaborating with academic institutions and experts to enhance technical expertise Utilizing professional consulting services for specialized support |
| Coordination issues | Establishing clear communication channels and regular coordination meetings Enhancing interdepartmental collaboration and information sharing Implementing effective project management tools and systems for better coordination |
| Challenges | Solutions |
| Lack of stakeholder buy-in and engagement | – Conducting extensive awareness campaigns and community outreach programs to educate stakeholders about the benefits of the CIDP Establishing platforms for meaningful participation and consultation with stakeholders throughout the planning and implementation process Incorporating feedback and addressing concerns raised by stakeholders |
| Political transitions and changes in leadership | – Ensuring continuity by institutionalizing the CIDP process and its objectives through legislation or policies Facilitating smooth transitions by documenting and sharing institutional knowledge and lessons learned Encouraging a culture of long-term planning and development beyond political cycles |
| Data and information gaps for evidence-based planning | – Conducting comprehensive data collection and analysis exercises to fill information gaps Collaborating with relevant research institutions and data providers to access reliable data Investing in data management systems and tools to ensure accurate and up-to-date information for decision-making |
| Resistance to change and reluctance to adopt new approaches | – Conducting awareness campaigns highlighting the need for change and the benefits of innovative approaches Providing capacity-building programs to empower stakeholders to embrace change and new methods Showcasing success stories and best practices from other counties to inspire confidence in new approaches |
| Monitoring and evaluation challenges | – Developing a robust monitoring and evaluation framework with clear indicators and targets Allocating resources for regular monitoring and evaluation activities Utilizing technology and data systems to streamline data collection, analysis, and reporting processes |
| Environmental and sustainability considerations | – Integrating environmental impact assessments into the CIDP process Promoting sustainable practices in infrastructure development and natural resource management Engaging environmental experts and stakeholders in the planning and implementation of environmental conservation initiatives |
These additional challenges and solutions provide a more comprehensive understanding of the potential obstacles that counties may encounter during CIDP implementation. By employing the suggested solutions, counties can address these challenges effectively and ensure the successful execution of their development plans.
Monitoring and Evaluation of County Integrated Development Plan (CIDP) Implementation
Monitoring and evaluation play a crucial role in ensuring effective implementation of the CIDP. Regular assessment of progress, impact, and outcomes helps identify bottlenecks, measure achievements, and make necessary adjustments. It enables counties to learn from their experiences, replicate successful models, and continuously improve their development interventions.
Benefits of County Integrated Development Plan (CIDP) Implementation:
This section discusses the advantages and positive outcomes that can be achieved through the successful implementation of the CIDP. It highlights the benefits such as improved infrastructure, enhanced service delivery, economic growth, and better quality of life for residents.
Achieving Sustainable Development through the CIDP:
This heading focuses on how the CIDP serves as a tool to promote sustainable development in counties. It explores how the plan addresses economic, social, and environmental aspects to ensure a balanced and sustainable approach to development.
Harnessing Agriculture and Rural Development in the CIDP:
This section focuses on the CIDP’s emphasis on agricultural development and rural growth. It explores strategies and interventions aimed at promoting agricultural productivity, value chain development, and inclusive rural development.
Enhancing Infrastructure Development through the CIDP:
The CIDP’s role in promoting infrastructure development. It discusses how the plan identifies and prioritizes infrastructure projects, including transportation networks, utilities, and public facilities, to support economic growth and improve connectivity.
Promoting Entrepreneurship and Job Creation in the CIDP:
This section explores how the CIDP can foster entrepreneurship and create employment opportunities. It discusses strategies and programs within the plan that support small business development, skills training, and job creation initiatives.
Success Stories of Counties with Effective CIDPs
Several counties have witnessed significant progress and positive change through the successful implementation of their CIDPs. These success stories demonstrate the transformative power of strategic planning and sustained commitment to development. They inspire and motivate other counties to invest in the formulation and implementation of their CIDPs.
Lessons Learned and Best Practices
Over the years, various lessons have been learned from CIDP processes across different counties. These lessons include the importance of robust stakeholder engagement, integration of cross-cutting issues such as gender and climate change, effective resource mobilization, and results-oriented monitoring and evaluation. Sharing these lessons and adopting best practices can enhance the quality and impact of CIDPs across counties.
Future Outlook for County Development
As counties continue to refine their CIDPs and align them with national and global development agendas, the future looks promising. With increased citizen participation, improved governance structures, and enhanced resource mobilization, counties are well-positioned to achieve sustainable and inclusive development.
Conclusion
The County Integrated Development Plan is a powerful tool that shapes the development trajectory of a county. It provides a roadmap for sustainable growth, empowers local communities, and fosters accountability and transparency. By investing in the formulation and implementation of CIDPs, counties can pave the way for a prosperous and equitable future.
In conclusion, the County Integrated Development Plan is a strategic document that outlines the development objectives, priorities, and strategies of a county. It serves as a roadmap for sustainable growth and guides the county’s decision-making processes. Through citizen participation, effective implementation, and continuous monitoring, CIDPs contribute to the overall development and progress of counties. By investing in their CIDPs, counties can shape a better future for their residents and create opportunities for inclusive and equitable development.
FAQs
01. What is the duration of a County Integrated Development Plan?
The County Integrated Development Plan covers a medium-term period of five years.
02. Who is involved in the CIDP process?
The CIDP process involves various stakeholders, including county governments, local communities, civil society organizations, and development partners
03. How does the CIDP promote citizen participation?
The CIDP encourages citizen engagement by providing platforms for residents to contribute their ideas, opinions, and feedback on the development agenda of their county.
04. How are development priorities and strategies determined in a CIDP?
Development priorities and strategies in a CIDP are determined through a thorough analysis of the county’s needs, strengths, weaknesses, and opportunities. This analysis involves extensive research, consultations with stakeholders, and consideration of national and global development goals.
05. What are some common challenges faced during CIDP implementation?
Common challenges during CIDP implementation include limited financial resources, capacity constraints within the county government, coordination issues among stakeholders, and the need to balance competing development priorities.
06. How is the progress of CIDP implementation monitored?
The progress of CIDP implementation is monitored through a robust monitoring and evaluation framework. This framework includes regular data collection, performance tracking, and impact assessments to measure the effectiveness of interventions and make informed decisions for improvement.
07. Can CIDPs be revised or updated during the implementation period?
Yes, CIDPs can be revised or updated during the implementation period. This flexibility allows counties to adapt to changing circumstances, incorporate new priorities, and refine strategies to ensure the plan remains relevant and effective.
08. Are there any success stories of counties with exemplary CIDP implementation?
Yes, several counties have achieved remarkable success through effective CIDP implementation. For example, County X successfully improved agricultural productivity and reduced poverty rates through targeted programs and investments in modern farming techniques. County Y enhanced tourism infrastructure and marketing strategies, resulting in a significant increase in visitor arrivals and revenue.
09. How can citizens contribute to the formulation of a CIDP?
Citizens can contribute to the formulation of a CIDP through public consultations, town hall meetings, and feedback mechanisms provided by the county government. They can share their ideas, concerns, and suggestions to ensure that the plan reflects their needs and aspirations.
10. What role do development partners play in CIDP implementation?
Development partners, such as international organizations and donor agencies, can provide technical and financial support to counties for CIDP implementation. They can assist in capacity building, knowledge sharing, and funding crucial development projects outlined in the plan.
11. How does the CIDP address environmental sustainability?
The CIDP includes strategies to promote environmental sustainability, such as conservation of natural resources, adoption of renewable energy sources, and the integration of climate change adaptation and mitigation measures into development programs. These efforts ensure that development is carried out in a way that protects the environment for future generations.
12. Can the CIDP be aligned with national and global development frameworks?
Yes, the CIDP can be aligned with national development frameworks, such as the National Development Plan, and international frameworks, such as the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). This alignment ensures that county-level development efforts contribute to broader national and global development agendas.
13. How are marginalized and vulnerable groups considered in the CIDP?
The CIDP recognizes the importance of inclusivity and social equity. It includes strategies to address the needs of marginalized and vulnerable groups, such as women, youth, persons with disabilities, and ethnic minorities. This ensures that development benefits reach all segments of the population, promoting social justice and reducing inequalities.